Delving into the intricacies of share splits and their implications, this guide offers a detailed exploration of this financial phenomenon. From understanding the basics to analyzing historical trends, readers are in for an enlightening journey through the world of share splits.
Exploring the impact on share prices, investor perception, and historical analysis, this guide aims to provide valuable insights for both novice and seasoned investors alike.
Overview of Share Splits
A share split, also known as a stock split, is a corporate action where a company divides its existing shares into multiple shares. This results in a decrease in the share price while maintaining the same market capitalization.
Share Split Ratios
Common share split ratios include 2-for-1, 3-for-1, or even higher multiples. For example, in a 2-for-1 split, each shareholder receives two shares for every share they previously owned, effectively doubling the number of shares outstanding.
Motivation for Share Splits
- Increased Liquidity: By reducing the share price, share splits make the stock more affordable for retail investors, potentially increasing trading volume and liquidity.
- Market Perception: A lower share price after a split may attract new investors who perceive the stock as more affordable and accessible.
- Psychological Impact: Share splits can create a positive psychological effect among investors, boosting confidence in the company's performance.
Impact on Share Price
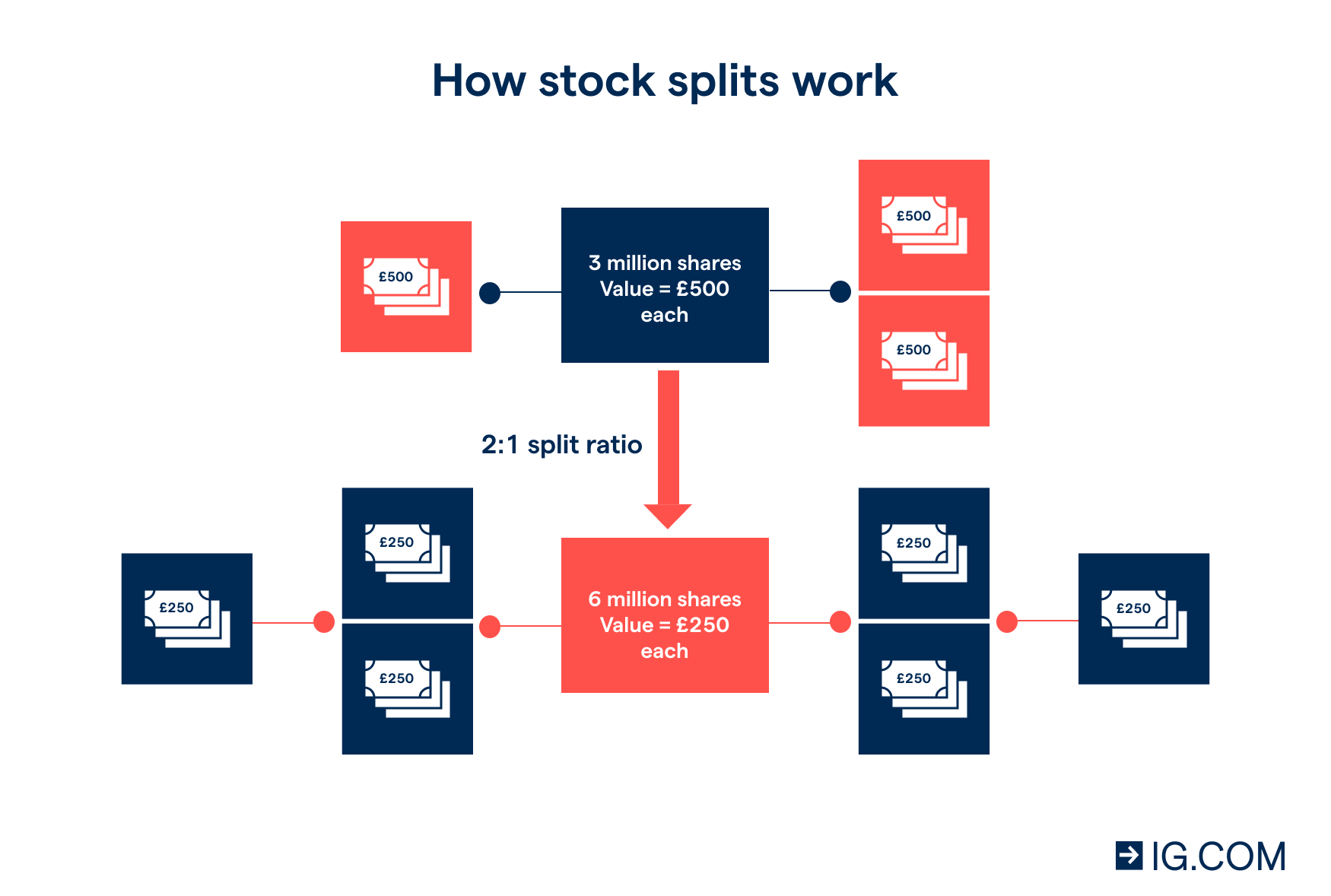
When a company decides to implement a share split, it can have a direct impact on the market price of the stock. This impact is primarily seen in the form of a decrease in the price per share after the split takes place.
However, the total value of the investor's holdings remains the same despite the change in the number of shares owned.
Market Capitalization Before and After a Share Split
Before a share split, the market capitalization of a company is calculated by multiplying the current price per share by the total number of outstanding shares. After a share split, the number of outstanding shares increases, while the price per share decreases.
As a result, the market capitalization remains the same both before and after the split. This means that the overall value of the company as perceived by the market does not change due to a share split.
Impact on Individual Investors vs. Institutional Investors
Individual Investors
Individual investors may perceive a share split as a positive event, as it allows them to purchase more shares at a lower price. This can potentially attract more retail investors to the stock, driving up demand and increasing liquidity in the market.
Institutional Investors
For institutional investors, the impact of a share split is often more muted. Since institutional investors typically deal in large volumes of shares, the decrease in price per share post-split may not have a significant impact on their overall investment strategy.
However, they may still adjust their positions based on market conditions and the implications of the split on the company's share price performance.
Investor Perception and Implications
When a company decides to undergo a share split, it can have a significant impact on investor sentiment and perception of the stock. Share splits are often viewed positively by investors as they can signal that the company's stock price has been performing well and is expected to continue to do so in the future.
This can create a sense of confidence among existing shareholders and attract new investors who may see the lower share price as more affordable and accessible.
Influence on Investor Sentiment
Share splits can influence investor sentiment by creating a perception of growth and stability within the company. Investors may interpret a share split as a sign that the company is confident in its future prospects, leading to increased trust in the stock.
This positive sentiment can drive up demand for the shares, potentially leading to an increase in the stock price post-split.
Psychological Impact on Investors
The psychological impact of a share split on both existing and potential investors can be significant. Existing shareholders may feel a sense of pride and ownership as their number of shares increase, even though the overall value remains the same.
On the other hand, potential investors may see a lower share price as an opportunity to enter the market and invest in a company that appears to be on an upward trajectory.
Examples of Significant Stock Price Changes
Several companies have experienced significant stock price changes following a share split. For instance, Apple conducted a 7-for-1 stock split in 2014, which led to a surge in the stock price over the following years. Similarly, Amazon's 3-for-1 stock split in 1999 resulted in a substantial increase in the stock price as investor confidence grew in the company's growth potential.
These examples illustrate how share splits can have a direct impact on investor perception and the stock's performance.
Historical Analysis
When examining the historical trends of companies that have undergone share splits, it becomes evident that there are certain patterns and outcomes that are commonly observed in the stock performance post-share split. These trends can give us valuable insights into the long-term implications of share splits on company valuation.
Trend Analysis of Companies Post-Share Splits
- Companies that have historically undergone share splits often experience a temporary surge in their stock price immediately following the split. This surge is typically attributed to the increased affordability of the shares, attracting more investors to purchase.
- However, this initial spike in stock price is usually short-lived, and the stock tends to stabilize or even dip slightly in the weeks following the split. This phenomenon is known as the "post-split depression" and is a common occurrence in many share splits.
- Over the long term, companies that have split their shares tend to see an overall increase in their market capitalization, as the increased number of outstanding shares can attract more investors and improve liquidity in the market.
Company Valuation After Share Splits
Share splits can have a significant impact on how analysts and investors perceive a company's valuation. While the actual value of the company remains unchanged post-split, the perception of a lower share price can sometimes attract more retail investors who may view the stock as more affordable.
It is essential for companies to carefully consider the timing and implications of a share split, as it can influence how the market perceives their growth potential and overall financial health.
Last Recap
In conclusion, the discussion on interpreting share splits and their implications unveils a complex yet intriguing aspect of the stock market. By grasping the nuances of share splits, investors can make informed decisions that may shape their investment journey for years to come.
FAQs
What is a share split?
A share split, also known as a stock split, is when a company divides its existing shares into multiple shares to boost liquidity and make them more affordable for investors.
How does a share split impact market price?
A share split typically leads to a decrease in the stock price while increasing the number of shares outstanding, maintaining the overall market capitalization of the company.
Can individual investors and institutional investors be affected differently by a share split?
Individual investors may view a share split positively as it makes shares more affordable, while institutional investors may not be significantly impacted due to their large investment capacities.